How is holographic paper made?
Here at AR Metallizing, we’re passionate about holography.
Holography gives unique and exciting looks to packaging and labels, and it can also offer anti-counterfeit features, for brands looking to protect their products from being copied.
So, while it’s both practical and beautiful, how is it made, and how are the different looks achieved?
How is holographic paper made?
Despite it looking very different from metallized paper, much of the process to manufacture holographic papers is actually the same. Here’s how the process works:
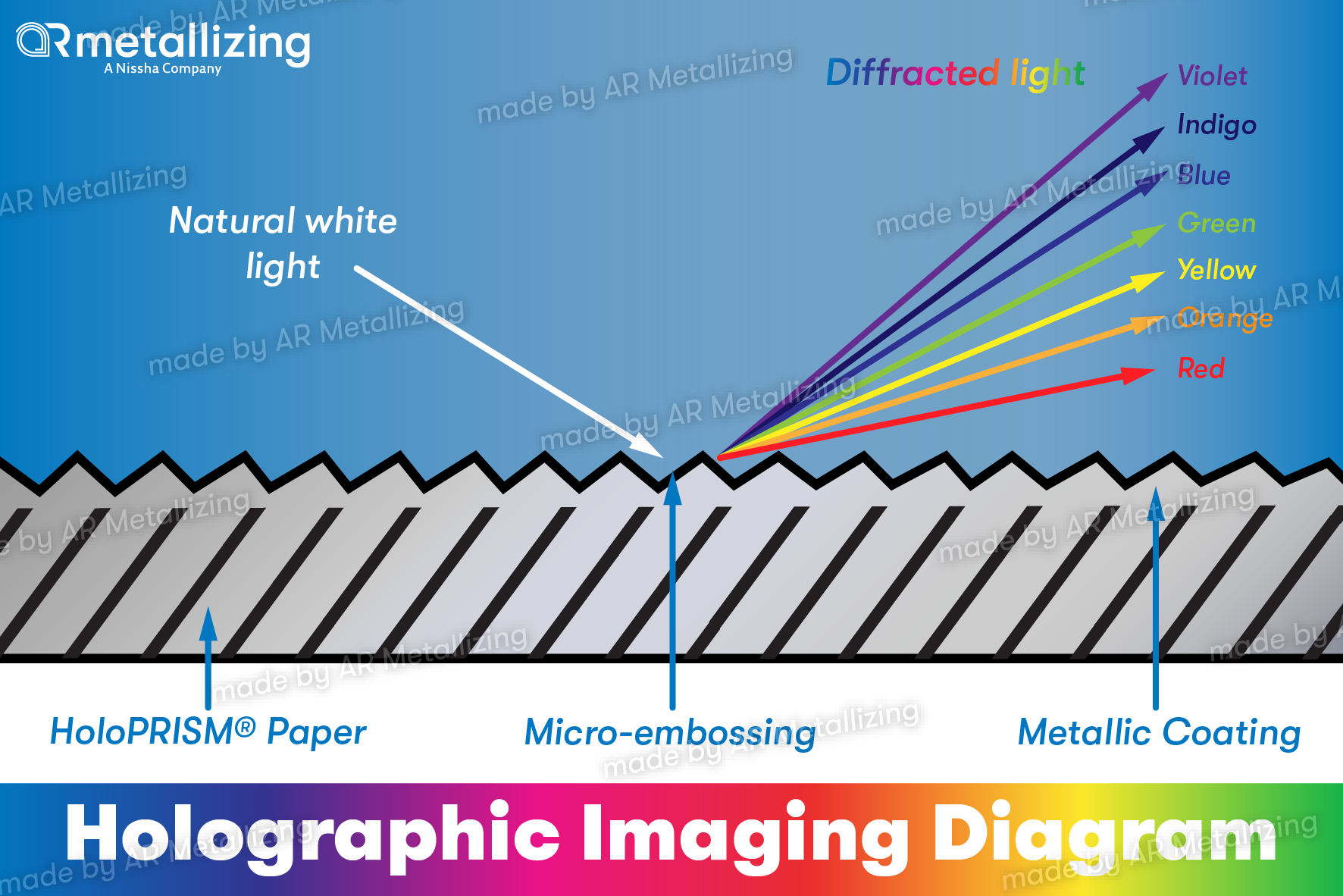
- Plain paper is embossed, either with a unique design, or with a pattern from our library of designs. The embossing process effectively alters the surface of the paper, changing it from completely smooth to ‘uneven’. It is this uneven surface (which is actually the design or pattern) which will create light diffraction when the paper is metallized.
- The embossed paper is then metallized. In this process, a microscopically thin layer of aluminum is vaporized onto the embossed paper. The sum thickness of this paper is only 20 to 30 nanometers thick. As natural white light hits the indentations and hollows in the embossed metallized surface, they diffract light, creating the effects we recognize as holography.
- A topcoat of lacquer is then added. This conditions the paper and effectively seals the metallization, to finish the holographic manufacturing process.
Despite holography adding very exciting designs and sensational looks to packaging and labels, our papers are 100% recyclable, making them an eco-friendly choice. AR Metallizing has a pattern book of nearly 100 standard patterns that our customers can choose from. Equally, we are also able to incorporate unique artwork, designs or elements (such as logos) into our holography for totally exclusive designs.